| This documentation is out of date.
The new version of the documentation is here: https://cannylogic.com/docs |
Difference between revisions of "Right rotation"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
!colspan="2" style="background-color:#AFEEEE;"|Appearance | !colspan="2" style="background-color:#AFEEEE;"|Appearance | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" align="center" style="padding:10px;"|[[File: | + | |colspan="2" align="center" style="padding:10px;"|[[File:5_4_8_2.png]] |
|- | |- | ||
!colspan="2" style="background-color:#AFEEEE;"|Symbol | !colspan="2" style="background-color:#AFEEEE;"|Symbol | ||
Latest revision as of 18:31, 23 November 2015
| Appearance | |
|---|---|
| |
| Symbol | |
| RSR | |
| Group | |
| Bitwise operators | |
| Inputs | |
| Value: | Integer |
| Shift, bits: | Integer |
| outputs | |
| Result: | Integer |
| Version CANNY Lab | |
| from 1.8b | |
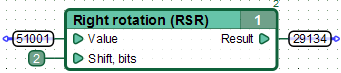
Circular shift to the right. Set the output result as the logical right shift in binary representation of the input "Value", the number of bits to shift specified by the input "Shift, bits", while leaving bit appears in place of free pop spot on the other end of the number.
In other words, the result is equivalent to the result of copying each bit in binary representation of input "value" to its right position, to the number of times specified by the value of the input "Shift, bits". Thus, the most significant (left-most) bit in the binary representation each time will have a value equal to the outgoing (least significant, extending to the right) bit of input value.
For example:
| Value | = | 51000 | = | 0xC738 | = | 0b1100011100111000 |
| Shift, bits | = | 2 | ||||
| Result | = | 12750 | = | 0x31CE | = | 0b0011000111001110 |
Features
Circular shift of 16-bit value in either direction for 8-bit, reverses its upper and lower bytes.