| This documentation is out of date.
The new version of the documentation is here: https://cannylogic.com/docs |
Difference between revisions of "CANNY 7"
| [unchecked revision] | [checked revision] |
(→Presentation of the functional diagram) |
(→Specifications) |
||
| (107 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''CANNY 7''' — miniature [[PLC | programmable logic controller]] designed for automotive, domestic and industrial use | + | '''CANNY 7''' — miniature [[PLC | programmable logic controller]] designed for automotive, domestic and industrial use. |
== General Information == | == General Information == | ||
| − | Due to limited external channels, programmable logic controller CANNY7 may be attributed to a class of smart relays or Nano PLC. | + | Due to limited external channels, programmable logic controller CANNY7 may be attributed to a class of smart relays or Nano PLC. CANNY7 is capable of solving many automation, controlling and monitoring tasks. |
CANNY7 is the first programmable logic controller oriented for automotive applications, with the following unique features and combination: | CANNY7 is the first programmable logic controller oriented for automotive applications, with the following unique features and combination: | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
*the maximum output current of each of the 11 IO channels +/- 120mA, sufficient to control usual automotive relay; | *the maximum output current of each of the 11 IO channels +/- 120mA, sufficient to control usual automotive relay; | ||
*CAN 2.0B Interface, compliant with ISO-11898, SAE J2411 widely used in modern cars; | *CAN 2.0B Interface, compliant with ISO-11898, SAE J2411 widely used in modern cars; | ||
| − | *built-in energy consumption management in the range of 5 to 60 mA, helps conserve battery power during | + | *built-in energy consumption management in the range of 5 to 60 mA, helps to conserve battery power during period of inactivity in a car; |
| − | *EEPROM for applications and sixty-four 16-bit | + | *EEPROM for applications and sixty-four 16-bit non-volatile memory data cells, available to user application to preserve critical data during a power failure; |
*wide operating temperature ranged from -40 to + 85 ° C; | *wide operating temperature ranged from -40 to + 85 ° C; | ||
*Integrated surge protection and short circuit protection | *Integrated surge protection and short circuit protection | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
*specialised packages of system and application software to use with automotive CAN and LIN networks. | *specialised packages of system and application software to use with automotive CAN and LIN networks. | ||
| − | To develop custom software for CANNY7, | + | To develop custom software for CANNY7, use graphical programming language CFD to quickly create user-effective applications- Functional Diagrams. The free of charge IDE CannyLab contains tools for editing, debugging and writing software to the controller. |
| + | |||
Requirements for writing software to the controller: | Requirements for writing software to the controller: | ||
*PC with a USB port version 1.1 or higher | *PC with a USB port version 1.1 or higher | ||
| − | *Installed CannyLab | + | *Installed CannyLab IDE |
*Ordinary miniUSB cable | *Ordinary miniUSB cable | ||
| − | Controllers' memory | + | Controllers' memory accessible to user is enough to accommodate the program, consisting of several hundred functional blocks, which allows for fairly sophisticated algorithms. |
Each of the 11 IO channels are able to operate in any of the 98 modes that define the voltage, current, and temporal parameters of the input and output signals. In addition, some of the channels can be configured to operate in digital mode, to transmit / receive data of such protocols as 1-Wire, I2C, RS-232, LIN, CAN. The configuration of each channel can be set and adjusted from the user application. | Each of the 11 IO channels are able to operate in any of the 98 modes that define the voltage, current, and temporal parameters of the input and output signals. In addition, some of the channels can be configured to operate in digital mode, to transmit / receive data of such protocols as 1-Wire, I2C, RS-232, LIN, CAN. The configuration of each channel can be set and adjusted from the user application. | ||
Two-coloured LEDs, controlled from the user application, are useful to indicate controller or debugging mode. | Two-coloured LEDs, controlled from the user application, are useful to indicate controller or debugging mode. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 38: | ||
*External connector X3 has three terminals, channels accordingly- №8, №9 and №10. Internal connector USB1 is to connect controller to the PC with miniUSB cable. | *External connector X3 has three terminals, channels accordingly- №8, №9 and №10. Internal connector USB1 is to connect controller to the PC with miniUSB cable. | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[File:6_2_1_1.png|800px]] |
=== Software Architecture === | === Software Architecture === | ||
| − | CANNY 7 is a digital programmable computing control device | + | CANNY 7 is a digital programmable computing control device. CANNY 7 main structural elements are: arithmetic logic unit (ALU), internal memory, commands execution management subsystem and input-output system. |
| − | [[ | + | [[File:6_2_2_1.png|800px]] |
| − | Arithmetic Logic Unit is processing core of CANNY 7. ALU provides system software and user functional execution diagram placed into the internal memory of the controller. | + | Arithmetic Logic Unit is the processing core of CANNY 7. ALU provides system software and user functional execution diagram placed into the internal memory of the controller. |
Controller's internal memory is divided into the EEP program memory, EEP data memory, and ROM. The command's management subsystem is responsible for switching and setting mode of the controller. The IO system provides controllers' communication to the outside world, using both discrete IO channels and standard digital interfaces CAN / LIN / RS232 / USB. | Controller's internal memory is divided into the EEP program memory, EEP data memory, and ROM. The command's management subsystem is responsible for switching and setting mode of the controller. The IO system provides controllers' communication to the outside world, using both discrete IO channels and standard digital interfaces CAN / LIN / RS232 / USB. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 52: | ||
<div style="float:left;padding-right:1em;"> | <div style="float:left;padding-right:1em;"> | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[File:6_2_3_1.png|250px]] |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | Software CANNY 7 consists of: a | + | Software CANNY 7 consists of: a bootloader, system software (operating system and drivers), and a custom function diagram. |
| − | The | + | The bootloader provides the controller with the software download mode, organising data transmission between CANNY 7 and PC using USB protocol. It checks the data integrity transmitted from the PC and loading to the controllers' internal memory. The bootloader placed into the internal memory of the controller during production and can not be deleted or modified by the user. The manufacturer distributes CANNY 7 firmware in CCX file format. It includes an operating system and a set of drivers providing function diagram execution and its interaction with the controllers' resources. The contents of various CCX files can be reloaded into the controller by user but user is restricted to modify CCX file content. |
| − | + | ||
| + | Custom block diagram is created and modified in CannyLab IDE, then it can be loaded into the controller where it specifies the algorithm to work standalone or saved in to CFD file. | ||
<br clear="all"> | <br clear="all"> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 65: | ||
There are several operation modes to perform basic operations with controller. | There are several operation modes to perform basic operations with controller. | ||
| − | === Software | + | === Software upload mode === |
| − | In this mode, the controller is running | + | In this mode, the controller is running bootloader to load firmware, and functional diagram under CannyLab management. Controller switch to this mode automatically when connected to PC with USB cable. During the transition to SW upload mode the controller performs a master reset: the functional diagram execution stops, IO channels are switching to neutral state, built-in green LED turns on. When controller establishes communicating with the PC software, the green LED goes into flickering mode. Exit from this mode happens automatically when the connection to the PC is disrupted. At the end of the software download mode , if EEPROM system software is loaded correctly, the controller will switch to running mode, otherwise it returns to SW download mode. |
| − | === | + | === Running mode === |
| − | + | Running mode is the main controllers' mode. In this mode, the controller is running continuously under system software sequence, in an endless cycle, performing the functional diagram, working on the algorithm specified by the user. Transition to this mode takes place automatically when the controller is connected to an external 12V power supply and the absence of the USB connection. | |
| − | When operating in this mode, the functional diagram has access to all resources of the controller | + | When operating in this mode, the functional diagram has access to all resources of the controller and drivers included in the controllers' system software. |
| − | |||
=== Sleep mode === | === Sleep mode === | ||
| − | This mode is an option of normal | + | This mode is an option of normal running mode in which, after each cycle of execution of a function diagram, the controller pauses to reduce its power consumption to a minimum. Thus, the controller operates in a pulsed mode, periodically "asleep" and "waking up". Enable, disable, and configure the parameters of this mode are controlled by the functional diagram. Using this mode is relevant when developing systems, focused on battery-power, such as the on-board car equipment. |
== Runtime Environment == | == Runtime Environment == | ||
| Line 83: | Line 84: | ||
The graphical block diagram developed in CannyLab environment, automatically processed by the translator just before loading to the controller. CannyLab checks on the consistency of the diagram, determines function blocks execution order and converts the diagram into the executable code - a sequence of machine instructions CANNY 7 controllers' ALU. | The graphical block diagram developed in CannyLab environment, automatically processed by the translator just before loading to the controller. CannyLab checks on the consistency of the diagram, determines function blocks execution order and converts the diagram into the executable code - a sequence of machine instructions CANNY 7 controllers' ALU. | ||
| − | === The | + | === The execution order === |
<div style="float:left;padding-right:1em;"> | <div style="float:left;padding-right:1em;"> | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[File:6_4_2_1.png|450px]] |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | + | Executable program code during loading into the controller already contained system software, is including in the sequence of the system software machine instructions. Thus, the aggregate command sequence loaded with system software and functional diagram, will be: initialisation routines executed once after each controllers' reset and executable functional diagram code, framed with the controller resources' procedure management, and placed in an infinite executable loop - diagrams running loop. Some of the drivers included in the controller system software, such as CAN driver, require controller to raise immediate response during data transmission and reception of program events. Program code of these drivers asynchronously processed by the controller in parallel with the main execution flow. In the processing of asynchronous drivers calls, the diagrams main run loop performance is briefly suspended. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<br clear="all"> | <br clear="all"> | ||
=== Access to hardware resources === | === Access to hardware resources === | ||
| − | + | All available resources to the user from the functional diagram : the system resources of the controller, IO subsystem and additional drivers included in the system software, appears on a controllers' internal memory protected address space. This address space is divided into read-only registers and write-only registers. | |
| − | + | The user is able to specify the read-only register address as a source of input data from virtually any function block of a diagram. Thereby extract and use to implement their own algorithms, data received by the controller from the outside world. For example information about the electric potential on any controllers' terminal, or the data packet contents received from the CAN bus. Write-only register address can be used as the output target for any functional block on the diagram. Thus, the user controls the resources of the controller from functional diagrams which gives an opportunity to influence the objects of the outside world. For example: switch external relay by changing the electrical potential on one of the pins of the controller, turn LED on; set CAN operation mode; send a data packet. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The most resources used include assignment required operating parameters, such as the polarity of the output channels, the polarity and the sensitivity of the input channels, CAN communication speed and so on. | |
| − | + | Specifying these parameters is made in the form of recording specific constants in one or a few specific registers, depending on a required set of resources configuration. For example, copying a constant with a value of 121 in the register located at 2432 address is set channel №0 to an output positive polarity mode. | |
| − | [[ | + | [[File:6_4_3_1.png|center]] |
| − | + | In CannyLab IDE, for user convenience, all the of the controllers' available registers are named, as well as all special constants that are used in interaction with the controllers' resources. Therefore, for CannyLab user this operation will look as setting the constants named [[CANNY_7,_Discrete_IO_Driver|"Default Positive Output"]] at the input of the function block "Copy" and setting the address with the name [[CANNY_7,_Discrete_IO_Driver|"Discrete Input/Output Mode Setup Register, IO Channel №0"]] at its output. | |
| − | [[ | + | [[File:6_4_3_2.png|center]] |
| − | + | Having thus established channel №0 mode, by the appearance of the value "1" in the register located at 2465 address ([[CANNY_7,_Discrete_IO_Driver|"Discrete Input Value Register, IO Channel №0"]]), we can learn about the application of a positive electric potential to №1 terminal of X2 connector. | |
| − | == | + | == Controllers' Registers == |
=== System Registers === | === System Registers === | ||
| − | :'' | + | :''Main article'': '''[[CANNY 7, System Registers]]''' |
| − | + | System resources are divided into an address group of read registers and an address group of write registers. Referring to the given registers from the functional diagram, you can get demanding information for practical application about the current status of the controller, and control its operational mode. The set of system registers located in the "System Registers" directory of CannyLab IDE registers list are accessible via "Input Register" and "Output Register" context menu. | |
=== Discrete Inputs and Outputs === | === Discrete Inputs and Outputs === | ||
| − | :'' | + | :''Main article'': '''[[CANNY 7, Discrete IO Driver]]''' |
| − | + | CANNY 7 users have access to eleven discrete general purpose IO channels. Each channel is physically available through corresponding pins of X2 and X3 connectors. Writing and reading data of the respective drivers registers, the functional diagram can manage the electric potential in each of these contacts and getting information about the current potential of each of them. | |
| + | The channel physical characteristics allow connection to a variety of external actuators such as: electromagnetic relays, small electric motors, LEDs. As an external digital input signal, it is possible to use a mechanical, electromechanical, and electronic buttons and switches, pulse generators, voltage source 0-12V and transistor outputs of various equipment, etc. | ||
| − | + | Channels operation mode and parameters specified by function diagram. At any given time, the channel can only work in one of the possible modes, but it is possible to dynamically override the channel configuration from the functional diagram. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
=== High Resolution PWM === | === High Resolution PWM === | ||
| − | :'' | + | :''Main article'': '''[[CANNY 7, HR PWM Driver]]''' |
| − | + | Two of the eleven IO channels (Channel №1 and №2) CANNY 7 are able to work in high-resolution pulse-width modulator mode. The channels may be activated independently of each other and have a configuration independent duty cycle and line pull-up, however, the high-resolution PWM period is a common parameter to both channels. In HR PWM mode, the PWM timing parameters - the period and duty cycle are set in the range of from 2 to 20,000 microseconds, in 1 microsecond increments. | |
| − | + | HR PWM channel has a fixed pulse polarity - GND 100mA. Generation can be conducted in either open collector (no pull-up or external pull-up) or with the internal pull-up to +12V (specified by setting value in the appropriate register ). In this mode, the channel is asynchronous to functional diagram, which allows for maximum stability of generated signal timing parameters. | |
{| | {| | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|'' | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|''Note:'' |
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|'' | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|''In the high-resolution pulse width modulator the electrical short circuit protection is disabled! Overload or channels short circuit being in RF PWM mode can cause damage to controller!'' |
|} | |} | ||
=== UART / RS232 / Modbus driver === | === UART / RS232 / Modbus driver === | ||
| − | :'' | + | :''Main article'': '''[[CANNY 7, UART Driver]]''' |
| − | + | Two of eleven IO channels (#9 and #10) CANNY 7 supports '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_asynchronous_receiver/transmitter UART]''', '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RS-232 RS-232]''' serial protocols data transmission/reception. It may be used to connect the controllers with each other or with external equipment supporting this communications protocols. The channels may be activated independently of each other and have individual data speed setting, protocol type and configuration, pull up line. | |
| − | + | '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_asynchronous_receiver/transmitter UART]''' implementation in CANNY 7 controllers allows to organize serial data reception and transmission over a single wire in half-duplex mode. Thus CANNY7 may have two independent connections using the | |
| + | '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_asynchronous_receiver/transmitter UART]''' protocol. Monitoring of the data link status should be done from the functional diagram. If the channel is free, the device may start data transmission , otherwise the device should wait for the line release. | ||
| − | + | '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RS-232 RS-232]''' implementation by using both '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_asynchronous_receiver/transmitter UART]''' data channels , allows to exchange data with other '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RS-232 RS-232]''' device in a duplex mode, i.e. one channel to perform data sending and on the other to simultaneously receive data. | |
| − | + | '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modbus Modbus]''' protocol in CANNY7 controllers are implemented as over '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_asynchronous_receiver/transmitter UART]''' or as over '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RS-232 RS-232]'''. As ADU (Application Data Unit) used compact binary option Modbus RTU. Checking the data integrity carried out by automatically calculated checksum (CRC). Package size is limited to 16 bytes including the CRC. | |
{| | {| | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|'' | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|''Note:'' |
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|'' | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|''For correct operation of all protocols based on the UART / RS-232 requires that all GND terminals of the devices committing communication, were given to a single potential ("common ground"). '' |
|} | |} | ||
{| | {| | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|'' | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|''Note:'' |
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|'' | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|''In UART implementation-active line is the potential GND 100mA, passive - positive potential of a given internal or external channel pull-up. In implementing RS-232 - the potentials inverse.'' |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | Driver '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_asynchronous_receiver/transmitter UART]'''/'''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RS-232 RS-232]'''/'''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modbus Modbus]''' operates using controllers' channels resources, but has a higher priority than a discrete input-output driver. Thus, upon activation of '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_asynchronous_receiver/transmitter UART]'''/'''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RS-232 RS-232]'''/'''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modbus Modbus]''' driver, for channels involved in its operation, a value changes in registers associated with discrete input-output driver, will be ignored. | |
=== CAN driver === | === CAN driver === | ||
| − | :'' | + | :''Main article'': '''[[CANNY 7, CAN Driver]]''' |
| − | + | Two special external terminals of CANNY 7 controller, located on pins 1 & 2 of X1 connector: CAN-H and CAN-L, designed for connection to '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAN_bus CAN-bus]'''. | |
| − | + | ||
=== LIN driver === | === LIN driver === | ||
| − | :'' | + | :''Main article'': '''[[CANNY 7, LIN Driver]]''' |
| − | + | Two of eleven input-output channels of CANNY 7, which can be placed under control of UART/RS-232 driver (Channel №9 and №10), can be used to organize data reception and transmission as two independent '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Local_Interconnect_Network LIN]''' driver channels. | |
| − | + | LIN driver channels can be connected both together and individually, have individual baud rate settings , pull-up line and bus node type- MASTER or SLAVE. | |
| − | + | LIN driver in its operation uses the resources of controller channels, but has a higher priority than discrete input-output driver. Thus, upon LIN driver activation, for the involved channels in its operation, changing values in registers associated controllers' discrete input-output driver will be ignored. | |
| − | === | + | === I²C driver === |
| − | :'' | + | :''Main article'': '''[[CANNY 7, I²C Driver]]''' |
| − | + | Communication lines (SDA and SCL) can be assigned to any pair of channels CANNY 7 controller. At the same time, these channels should be pulled-up to 5V with resistor 1 - 10k Ohm from the outside. The peculiarity of '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I%C2%B2C I²C]''' protocol implementation is that CANNY 7 controller can act only as a Master node. Data exchange between devices, that can be both single and bi directional, takes place in separate sessions, i. e. opening multiple sessions with different devices is not allowed. The maximum length of the message within one session I²C of 16 bytes. Exchange rate is fixed to 100 kbit/s. The total number of slaves on the line can reach several tens. | |
| − | + | Driver I²C operates using controller channels' resources , but has a higher priority than discrete input-output driver. Thus, upon activation I²C driver, for channels involved in to its operation, change values in associated registers of discrete input-output driver, will be ignored. | |
=== Dallas 1-Wire driver === | === Dallas 1-Wire driver === | ||
| − | :'' | + | :''Main article'': '''[[CANNY 7, Dallas 1-Wire Driver]]''' |
| − | + | CANNY 7 controller can be used as a MASTER in a single-wire data network '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1-Wire Dallas® 1-Wire®]'''. | |
| − | + | Any of CANNY 7 input-output channels can be used to connect the controller to 1-Wire bus. At the same time, that channel must be externally pulled-up to 5V with resistor 3-7k Ohm. Consistently reassigning driver channels, it's possible to arrange up to 11 independent connections 1-Wire. Wherein device addressing and device handling by address is not available, therefore, in 1-Wire mode it is possible to connect only one SLAVE node at a time to controllers' channel. | |
| − | + | Driver Dallas 1-Wire in its operation uses controller channels' resources, but has a higher priority than discrete input-output driver.Thus, upon activation Dallas 1-Wire driver, for channels involved in to its operation, change values in associated registers of discrete input-output driver will be ignored. | |
| − | === | + | === User Preprogrammed Parameters === |
| − | :'' | + | :''Main article'': '''[[CANNY 7, User Preprogrammed Parameters]]''' |
| − | + | The custom configuration parameters can be specified by the end user while the controller is loading a software using [[Firmware Update Utility]]. After software downloading and controller run in standalone mode, parameters set by user become available in the relevant functional diagram of the controller registers. | |
| − | + | Proper use of user-defined parameters significantly increases the flexibility and versatility of the controller-based solutions, enabling the end user without the skills to work with CannyLab, make safe changes in controller operation algorithm, using a simple user interface. | |
| − | === EEPROM Non-volatile Memory | + | === EEPROM Non-volatile Memory === |
| − | :'' | + | :''Main article'': '''[[CANNY 7, EEPROM Driver]]''' |
| − | + | To eliminate loss of critical information (state of the controller, external devices status, and so on..) I case of power reset , CANNY7 controller equipped with non-volatile memory. The values saved in EEPROM will be available in special registers after the power is restored. | |
| − | + | There are 64 16-bit non-volatile memory cells, which are accessed by corresponding read and write registers. | |
{| | {| | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|'' | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|''Note:'' |
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|'' | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|''Working with non-volatile memory does not require any special pre-configuration.'' |
|} | |} | ||
=== Infrared Remote Control Driver === | === Infrared Remote Control Driver === | ||
| − | :'' | + | :''Main article'': '''[[CANNY 7, IRRC Driver]]''' |
| − | + | CANNY 7 controller can receive and send infrared remote controls commands (IRRC) in popular formats- NEC and extended NEC. Driver operation is possible in three modes: reception only,transmission only or reception / transmission. For transmission and reception any two channels can be used. | |
| − | + | When transmitting infrared remote control commands, channel used for this only generates baseband signal. To generate pulse packet, controller requires a carrier frequency, the source of which can be internal high frequency PWM channel or external PWM generator. Receiving IR command requires an external demodulator, such as TSOP1736 or similar. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | IRRC driver in its operation uses the resources of controller channels, but has a higher priority than discrete input-output driver. Thus, upon IRRC driver activation, for the involved channels in its operation, changing values in registers associated controllers' discrete input-output driver will be ignored. | |
== Specifications == | == Specifications == | ||
| Line 239: | Line 235: | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;" colspan="2"| | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;" colspan="2"|Supply voltage |
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|9...18 | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|9...18 V |
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"| | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|Current consumption: |
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"| | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|in operation (no more than) |
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|55 | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|55 mA |
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
|valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"| | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"| | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"| | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|in power saving mode (not more) |
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|5,5 | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|5,5 mA |
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;" colspan="2"| | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;" colspan="2"|The maximum current of each channel in output mode |
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|+120 | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|+120 mA / -120 mA |
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;" colspan="2"| | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;" colspan="2"|Channel resistance in input mode |
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|4 | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|4 K or 200 K |
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;" colspan="2"| | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;" colspan="2"|Operating temperature range |
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|-40<sup> | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|-40<sup>o</sup>С...+85<sup>o</sup>С |
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;" colspan="2"| | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;" colspan="2"|Ingress Protection Rating |
|valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|IP50 | |valign="top" style="padding-left:0.5em;"|IP50 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | Electrical circuits protection: | |
| − | * | + | *from channel short-circuit - software; |
| − | * | + | *from channel overload - internal current-limiting fusing resistors; |
| − | * | + | *from power supply reverse polarity - internal diode; |
| − | * | + | *high emissions suppression circuit during inductive loads switching on channels №0 to №7 - diode and varistor; |
| − | * | + | *high emissions suppression circuit during inductive loads switching on channels №8 to №10 — absent. |
=== Safety Precautions === | === Safety Precautions === | ||
| − | + | The circuits of the controller do not have life-threatening voltage. Controller open terminals are under voltage during operation. Any connections to the controller and maintenance are made only with the power off to the controller and connected devices.. | |
=== Installation and connection === | === Installation and connection === | ||
| − | + | Installation and connection of the controller must be carried out only by qualified personal studied this documentation. Controller installation must be carried out in suitable areas to operation conditions of the controller. | |
| − | + | Do not allow moisture comes in contact with output terminals and internal elements of the controller. It is forbidden to use the controller in the presence of ambient acids , alkalis, and other corrosive substances. | |
| − | + | Installing the controller and the cables laying connected to it must be done at a distance of not less than 0.3 meters from the high-voltage power lines and strong electromagnetic sources - power relays, contactors, gas discharge lamps. Avoid getting moisture on the controller enclosure at the installation site. | |
=== Transportation and storage === | === Transportation and storage === | ||
| − | + | Controllers transported by all types of covered transportation . Placing and securing the shipping container with the packed devices in vehicles must provide their stable position and to prevent movement during transport. | |
| − | + | Transportation and storage should be carried out at ambient temperatures from minus -40 to +85 ° C and relative humidity - up to 80%, compliance with security measures of protection from shock and vibration. The air must not contain acids, alkalis and other aggressive substances. Controllers should be stored on shelves. | |
Latest revision as of 22:57, 15 August 2020
CANNY 7 — miniature programmable logic controller designed for automotive, domestic and industrial use.
Contents
General Information
Due to limited external channels, programmable logic controller CANNY7 may be attributed to a class of smart relays or Nano PLC. CANNY7 is capable of solving many automation, controlling and monitoring tasks.
CANNY7 is the first programmable logic controller oriented for automotive applications, with the following unique features and combination:
- rated power supply and IO channels voltage 0 / 12V (18V max);
- the maximum output current of each of the 11 IO channels +/- 120mA, sufficient to control usual automotive relay;
- CAN 2.0B Interface, compliant with ISO-11898, SAE J2411 widely used in modern cars;
- built-in energy consumption management in the range of 5 to 60 mA, helps to conserve battery power during period of inactivity in a car;
- EEPROM for applications and sixty-four 16-bit non-volatile memory data cells, available to user application to preserve critical data during a power failure;
- wide operating temperature ranged from -40 to + 85 ° C;
- Integrated surge protection and short circuit protection
- compact housing compliant to IP50 enclosure protection specification, suitable for installation and operation as part of a car cabin equipment;
- specialised packages of system and application software to use with automotive CAN and LIN networks.
To develop custom software for CANNY7, use graphical programming language CFD to quickly create user-effective applications- Functional Diagrams. The free of charge IDE CannyLab contains tools for editing, debugging and writing software to the controller.
Requirements for writing software to the controller:
- PC with a USB port version 1.1 or higher
- Installed CannyLab IDE
- Ordinary miniUSB cable
Controllers' memory accessible to user is enough to accommodate the program, consisting of several hundred functional blocks, which allows for fairly sophisticated algorithms. Each of the 11 IO channels are able to operate in any of the 98 modes that define the voltage, current, and temporal parameters of the input and output signals. In addition, some of the channels can be configured to operate in digital mode, to transmit / receive data of such protocols as 1-Wire, I2C, RS-232, LIN, CAN. The configuration of each channel can be set and adjusted from the user application. Two-coloured LEDs, controlled from the user application, are useful to indicate controller or debugging mode.
Design and functional operation
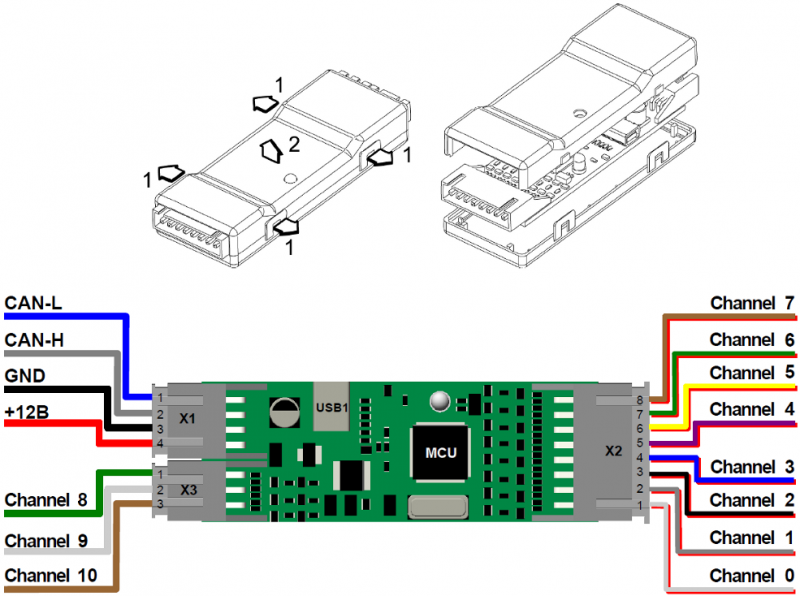
The appearance and layout
The main components of CANNY 7 are: a micro controller (MCU) with the auxiliary circuits, power supply system for all controllers' elements, IO channels level matching circuit, electric protection system, connectors and LED, based on a single print board 65 x 23 mm mounted inside a quick-open plastic casing. The controller has three external connectors and one internal. To connect the controller to the power supply and external devices, the kit includes a set of jumper harness.
- External connector X1 contains four terminals: + 12V input, power input GND, CAN-H and CAN-L.
- External connector X2 contains eight terminals, corresponding to the first eight channels of the controller, from №0 to №7.
- External connector X3 has three terminals, channels accordingly- №8, №9 and №10. Internal connector USB1 is to connect controller to the PC with miniUSB cable.
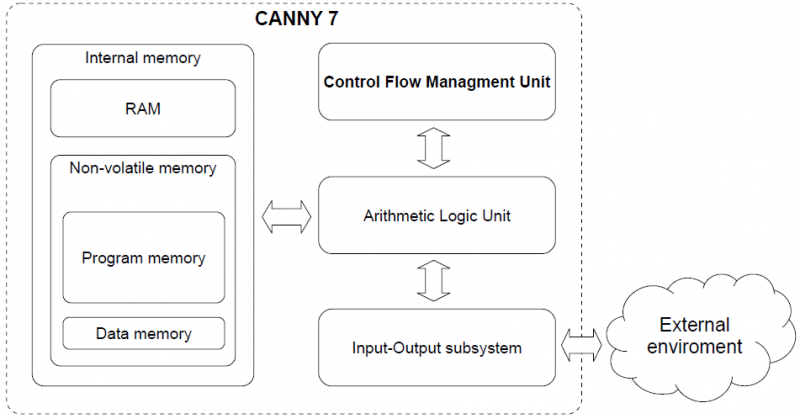
Software Architecture
CANNY 7 is a digital programmable computing control device. CANNY 7 main structural elements are: arithmetic logic unit (ALU), internal memory, commands execution management subsystem and input-output system.
Arithmetic Logic Unit is the processing core of CANNY 7. ALU provides system software and user functional execution diagram placed into the internal memory of the controller. Controller's internal memory is divided into the EEP program memory, EEP data memory, and ROM. The command's management subsystem is responsible for switching and setting mode of the controller. The IO system provides controllers' communication to the outside world, using both discrete IO channels and standard digital interfaces CAN / LIN / RS232 / USB.
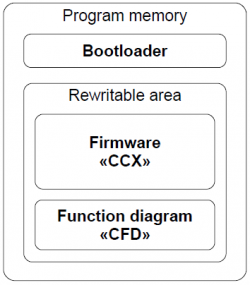
Software Structure
Software CANNY 7 consists of: a bootloader, system software (operating system and drivers), and a custom function diagram.
The bootloader provides the controller with the software download mode, organising data transmission between CANNY 7 and PC using USB protocol. It checks the data integrity transmitted from the PC and loading to the controllers' internal memory. The bootloader placed into the internal memory of the controller during production and can not be deleted or modified by the user. The manufacturer distributes CANNY 7 firmware in CCX file format. It includes an operating system and a set of drivers providing function diagram execution and its interaction with the controllers' resources. The contents of various CCX files can be reloaded into the controller by user but user is restricted to modify CCX file content.
Custom block diagram is created and modified in CannyLab IDE, then it can be loaded into the controller where it specifies the algorithm to work standalone or saved in to CFD file.
Operation modes
There are several operation modes to perform basic operations with controller.
Software upload mode
In this mode, the controller is running bootloader to load firmware, and functional diagram under CannyLab management. Controller switch to this mode automatically when connected to PC with USB cable. During the transition to SW upload mode the controller performs a master reset: the functional diagram execution stops, IO channels are switching to neutral state, built-in green LED turns on. When controller establishes communicating with the PC software, the green LED goes into flickering mode. Exit from this mode happens automatically when the connection to the PC is disrupted. At the end of the software download mode , if EEPROM system software is loaded correctly, the controller will switch to running mode, otherwise it returns to SW download mode.
Running mode
Running mode is the main controllers' mode. In this mode, the controller is running continuously under system software sequence, in an endless cycle, performing the functional diagram, working on the algorithm specified by the user. Transition to this mode takes place automatically when the controller is connected to an external 12V power supply and the absence of the USB connection. When operating in this mode, the functional diagram has access to all resources of the controller and drivers included in the controllers' system software.
Sleep mode
This mode is an option of normal running mode in which, after each cycle of execution of a function diagram, the controller pauses to reduce its power consumption to a minimum. Thus, the controller operates in a pulsed mode, periodically "asleep" and "waking up". Enable, disable, and configure the parameters of this mode are controlled by the functional diagram. Using this mode is relevant when developing systems, focused on battery-power, such as the on-board car equipment.
Runtime Environment
Functional diagram presentation
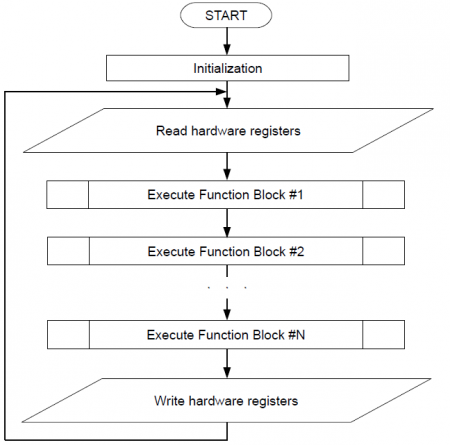
The graphical block diagram developed in CannyLab environment, automatically processed by the translator just before loading to the controller. CannyLab checks on the consistency of the diagram, determines function blocks execution order and converts the diagram into the executable code - a sequence of machine instructions CANNY 7 controllers' ALU.
The execution order
Executable program code during loading into the controller already contained system software, is including in the sequence of the system software machine instructions. Thus, the aggregate command sequence loaded with system software and functional diagram, will be: initialisation routines executed once after each controllers' reset and executable functional diagram code, framed with the controller resources' procedure management, and placed in an infinite executable loop - diagrams running loop. Some of the drivers included in the controller system software, such as CAN driver, require controller to raise immediate response during data transmission and reception of program events. Program code of these drivers asynchronously processed by the controller in parallel with the main execution flow. In the processing of asynchronous drivers calls, the diagrams main run loop performance is briefly suspended.
Access to hardware resources
All available resources to the user from the functional diagram : the system resources of the controller, IO subsystem and additional drivers included in the system software, appears on a controllers' internal memory protected address space. This address space is divided into read-only registers and write-only registers.
The user is able to specify the read-only register address as a source of input data from virtually any function block of a diagram. Thereby extract and use to implement their own algorithms, data received by the controller from the outside world. For example information about the electric potential on any controllers' terminal, or the data packet contents received from the CAN bus. Write-only register address can be used as the output target for any functional block on the diagram. Thus, the user controls the resources of the controller from functional diagrams which gives an opportunity to influence the objects of the outside world. For example: switch external relay by changing the electrical potential on one of the pins of the controller, turn LED on; set CAN operation mode; send a data packet.
The most resources used include assignment required operating parameters, such as the polarity of the output channels, the polarity and the sensitivity of the input channels, CAN communication speed and so on.
Specifying these parameters is made in the form of recording specific constants in one or a few specific registers, depending on a required set of resources configuration. For example, copying a constant with a value of 121 in the register located at 2432 address is set channel №0 to an output positive polarity mode.
In CannyLab IDE, for user convenience, all the of the controllers' available registers are named, as well as all special constants that are used in interaction with the controllers' resources. Therefore, for CannyLab user this operation will look as setting the constants named "Default Positive Output" at the input of the function block "Copy" and setting the address with the name "Discrete Input/Output Mode Setup Register, IO Channel №0" at its output.
Having thus established channel №0 mode, by the appearance of the value "1" in the register located at 2465 address ("Discrete Input Value Register, IO Channel №0"), we can learn about the application of a positive electric potential to №1 terminal of X2 connector.
Controllers' Registers
System Registers
- Main article: CANNY 7, System Registers
System resources are divided into an address group of read registers and an address group of write registers. Referring to the given registers from the functional diagram, you can get demanding information for practical application about the current status of the controller, and control its operational mode. The set of system registers located in the "System Registers" directory of CannyLab IDE registers list are accessible via "Input Register" and "Output Register" context menu.
Discrete Inputs and Outputs
- Main article: CANNY 7, Discrete IO Driver
CANNY 7 users have access to eleven discrete general purpose IO channels. Each channel is physically available through corresponding pins of X2 and X3 connectors. Writing and reading data of the respective drivers registers, the functional diagram can manage the electric potential in each of these contacts and getting information about the current potential of each of them. The channel physical characteristics allow connection to a variety of external actuators such as: electromagnetic relays, small electric motors, LEDs. As an external digital input signal, it is possible to use a mechanical, electromechanical, and electronic buttons and switches, pulse generators, voltage source 0-12V and transistor outputs of various equipment, etc.
Channels operation mode and parameters specified by function diagram. At any given time, the channel can only work in one of the possible modes, but it is possible to dynamically override the channel configuration from the functional diagram.
High Resolution PWM
- Main article: CANNY 7, HR PWM Driver
Two of the eleven IO channels (Channel №1 and №2) CANNY 7 are able to work in high-resolution pulse-width modulator mode. The channels may be activated independently of each other and have a configuration independent duty cycle and line pull-up, however, the high-resolution PWM period is a common parameter to both channels. In HR PWM mode, the PWM timing parameters - the period and duty cycle are set in the range of from 2 to 20,000 microseconds, in 1 microsecond increments.
HR PWM channel has a fixed pulse polarity - GND 100mA. Generation can be conducted in either open collector (no pull-up or external pull-up) or with the internal pull-up to +12V (specified by setting value in the appropriate register ). In this mode, the channel is asynchronous to functional diagram, which allows for maximum stability of generated signal timing parameters.
| Note: | In the high-resolution pulse width modulator the electrical short circuit protection is disabled! Overload or channels short circuit being in RF PWM mode can cause damage to controller! |
UART / RS232 / Modbus driver
- Main article: CANNY 7, UART Driver
Two of eleven IO channels (#9 and #10) CANNY 7 supports UART, RS-232 serial protocols data transmission/reception. It may be used to connect the controllers with each other or with external equipment supporting this communications protocols. The channels may be activated independently of each other and have individual data speed setting, protocol type and configuration, pull up line.
UART implementation in CANNY 7 controllers allows to organize serial data reception and transmission over a single wire in half-duplex mode. Thus CANNY7 may have two independent connections using the UART protocol. Monitoring of the data link status should be done from the functional diagram. If the channel is free, the device may start data transmission , otherwise the device should wait for the line release.
RS-232 implementation by using both UART data channels , allows to exchange data with other RS-232 device in a duplex mode, i.e. one channel to perform data sending and on the other to simultaneously receive data.
Modbus protocol in CANNY7 controllers are implemented as over UART or as over RS-232. As ADU (Application Data Unit) used compact binary option Modbus RTU. Checking the data integrity carried out by automatically calculated checksum (CRC). Package size is limited to 16 bytes including the CRC.
| Note: | For correct operation of all protocols based on the UART / RS-232 requires that all GND terminals of the devices committing communication, were given to a single potential ("common ground"). |
| Note: | In UART implementation-active line is the potential GND 100mA, passive - positive potential of a given internal or external channel pull-up. In implementing RS-232 - the potentials inverse. |
Driver UART/RS-232/Modbus operates using controllers' channels resources, but has a higher priority than a discrete input-output driver. Thus, upon activation of UART/RS-232/Modbus driver, for channels involved in its operation, a value changes in registers associated with discrete input-output driver, will be ignored.
CAN driver
- Main article: CANNY 7, CAN Driver
Two special external terminals of CANNY 7 controller, located on pins 1 & 2 of X1 connector: CAN-H and CAN-L, designed for connection to CAN-bus.
LIN driver
- Main article: CANNY 7, LIN Driver
Two of eleven input-output channels of CANNY 7, which can be placed under control of UART/RS-232 driver (Channel №9 and №10), can be used to organize data reception and transmission as two independent LIN driver channels.
LIN driver channels can be connected both together and individually, have individual baud rate settings , pull-up line and bus node type- MASTER or SLAVE.
LIN driver in its operation uses the resources of controller channels, but has a higher priority than discrete input-output driver. Thus, upon LIN driver activation, for the involved channels in its operation, changing values in registers associated controllers' discrete input-output driver will be ignored.
I²C driver
- Main article: CANNY 7, I²C Driver
Communication lines (SDA and SCL) can be assigned to any pair of channels CANNY 7 controller. At the same time, these channels should be pulled-up to 5V with resistor 1 - 10k Ohm from the outside. The peculiarity of I²C protocol implementation is that CANNY 7 controller can act only as a Master node. Data exchange between devices, that can be both single and bi directional, takes place in separate sessions, i. e. opening multiple sessions with different devices is not allowed. The maximum length of the message within one session I²C of 16 bytes. Exchange rate is fixed to 100 kbit/s. The total number of slaves on the line can reach several tens.
Driver I²C operates using controller channels' resources , but has a higher priority than discrete input-output driver. Thus, upon activation I²C driver, for channels involved in to its operation, change values in associated registers of discrete input-output driver, will be ignored.
Dallas 1-Wire driver
- Main article: CANNY 7, Dallas 1-Wire Driver
CANNY 7 controller can be used as a MASTER in a single-wire data network Dallas® 1-Wire®.
Any of CANNY 7 input-output channels can be used to connect the controller to 1-Wire bus. At the same time, that channel must be externally pulled-up to 5V with resistor 3-7k Ohm. Consistently reassigning driver channels, it's possible to arrange up to 11 independent connections 1-Wire. Wherein device addressing and device handling by address is not available, therefore, in 1-Wire mode it is possible to connect only one SLAVE node at a time to controllers' channel.
Driver Dallas 1-Wire in its operation uses controller channels' resources, but has a higher priority than discrete input-output driver.Thus, upon activation Dallas 1-Wire driver, for channels involved in to its operation, change values in associated registers of discrete input-output driver will be ignored.
User Preprogrammed Parameters
- Main article: CANNY 7, User Preprogrammed Parameters
The custom configuration parameters can be specified by the end user while the controller is loading a software using Firmware Update Utility. After software downloading and controller run in standalone mode, parameters set by user become available in the relevant functional diagram of the controller registers.
Proper use of user-defined parameters significantly increases the flexibility and versatility of the controller-based solutions, enabling the end user without the skills to work with CannyLab, make safe changes in controller operation algorithm, using a simple user interface.
EEPROM Non-volatile Memory
- Main article: CANNY 7, EEPROM Driver
To eliminate loss of critical information (state of the controller, external devices status, and so on..) I case of power reset , CANNY7 controller equipped with non-volatile memory. The values saved in EEPROM will be available in special registers after the power is restored.
There are 64 16-bit non-volatile memory cells, which are accessed by corresponding read and write registers.
| Note: | Working with non-volatile memory does not require any special pre-configuration. |
Infrared Remote Control Driver
- Main article: CANNY 7, IRRC Driver
CANNY 7 controller can receive and send infrared remote controls commands (IRRC) in popular formats- NEC and extended NEC. Driver operation is possible in three modes: reception only,transmission only or reception / transmission. For transmission and reception any two channels can be used.
When transmitting infrared remote control commands, channel used for this only generates baseband signal. To generate pulse packet, controller requires a carrier frequency, the source of which can be internal high frequency PWM channel or external PWM generator. Receiving IR command requires an external demodulator, such as TSOP1736 or similar.
IRRC driver in its operation uses the resources of controller channels, but has a higher priority than discrete input-output driver. Thus, upon IRRC driver activation, for the involved channels in its operation, changing values in registers associated controllers' discrete input-output driver will be ignored.
Specifications
Electrical characteristics and environmental requirements
| Supply voltage | 9...18 V | |
| Current consumption: | in operation (no more than) | 55 mA |
| in power saving mode (not more) | 5,5 mA | |
| The maximum current of each channel in output mode | +120 mA / -120 mA | |
| Channel resistance in input mode | 4 K or 200 K | |
| Operating temperature range | -40oС...+85oС | |
| Ingress Protection Rating | IP50 | |
Electrical circuits protection:
- from channel short-circuit - software;
- from channel overload - internal current-limiting fusing resistors;
- from power supply reverse polarity - internal diode;
- high emissions suppression circuit during inductive loads switching on channels №0 to №7 - diode and varistor;
- high emissions suppression circuit during inductive loads switching on channels №8 to №10 — absent.
Safety Precautions
The circuits of the controller do not have life-threatening voltage. Controller open terminals are under voltage during operation. Any connections to the controller and maintenance are made only with the power off to the controller and connected devices..
Installation and connection
Installation and connection of the controller must be carried out only by qualified personal studied this documentation. Controller installation must be carried out in suitable areas to operation conditions of the controller.
Do not allow moisture comes in contact with output terminals and internal elements of the controller. It is forbidden to use the controller in the presence of ambient acids , alkalis, and other corrosive substances.
Installing the controller and the cables laying connected to it must be done at a distance of not less than 0.3 meters from the high-voltage power lines and strong electromagnetic sources - power relays, contactors, gas discharge lamps. Avoid getting moisture on the controller enclosure at the installation site.
Transportation and storage
Controllers transported by all types of covered transportation . Placing and securing the shipping container with the packed devices in vehicles must provide their stable position and to prevent movement during transport.
Transportation and storage should be carried out at ambient temperatures from minus -40 to +85 ° C and relative humidity - up to 80%, compliance with security measures of protection from shock and vibration. The air must not contain acids, alkalis and other aggressive substances. Controllers should be stored on shelves.